When the Great War began, a grammar school boy from Newcastle upon Tyne who had gone into business as a shipper and trader in the far reaches of the British Empire, found himself in the skies above Flanders. Aviation was in its infancy, and every flight had an element of the experimental about it.
When Britain declared war on a Germany whose troops were already marching through Belgium in early August 1914, one Leonard Learmount, aged 25, was employed in the Straits Settlements (Malaya and Singapore), working for London-headquartered shipping and trading company Paterson Simons.

Life in the British Empire’s warmer climes was good for a young single man then, expat clubs providing social connections and sport.
Learmount had also joined the Malay States Volunteer Rifles (MSVR), a British overseas military reserve unit, as a Private Soldier. Nevertheless, following the outbreak of a war predicted to be “over by Christmas”, that November he took a ship back home to join up.

When he reported for military service he was chosen for training as a pilot in the Royal Flying Corps (RFC). It is not clear – historically at least – why the RFC decided he was suitable material, but given the indicators for other such personnel choices at the time, it’s probably because the MSVR had trained Learmount to ride and maintain a motorcycle. These skills, combined with his maths and physics education at the Royal Newcastle Grammar School, probably swung the decision.
Learmount reported to Brooklands aerodrome, Surrey, on 19 March 1915 for RFC flying training, and his flying log book says he got airborne the next day for his first lesson in a Maurice Farman “Longhorn” biplane, an ungainly French-designed machine.

His instructor, Sgt Watts, hadn’t been trained as an instructor, he merely had flying experience. The RFC hadn’t developed a flying training syllabus until early 1917, and didn’t begin formally training instructors until late 1917.
On 1 April 1915, Learmount flew a sortie lasting 45min, by far the longest duration trip he had flown. In the remarks column of his flying log book he wrote: “First time controlled machine from pilot’s seat. Did several landings. No wind – no bumps.”
The next day, he took off for his first solo flight at 6:15am, exactly two weeks after his very first flight. By that point Learmount had flown ten trips, all within sight of the airfield, and logged a total of 3h 10min in the air. The solo flight lasted 10min and was flown at 1,000ft – probably one circuit of Brooklands aerodrome. At 10:30am the same day, he got airborne for his flying test, which took 1hr exactly, and it earned him his “ticket” – his Royal Aero Club Aviator’s Certificate (Number 1147).
By the time he was dispatched to France on 12 June, Learmount’s entire pilot training had lasted 12 weeks exactly, about half of it flown on the Farman Longhorn, the remainder on the excitingly named Vickers Fighter – the FB5 – also known as the Vickers Gunbus. It was a two-seater “pusher” biplane which, in operation (not in training), was fitted with a Lewis machine gun at the forward crew position. Learmount’s flying training time had been divided about equally between the aerodromes at Brooklands, Surrey and Joyce Green, Kent in the Dartford marshes.
The question is, how were these newly trained pilots performing operationally when they arrived on the front in France? Major Raymond Smith-Barry – a graduate of the very first course at the Central Flying School, Upavon in 1912, had been serving as an RFC pilot in France from August 1914, and by 1916 he realised that the standard of flying among the arriving aviators was simply appalling, and he decided something had to be done. By late 1916 he had compiled a formal training syllabus, which he first introduced at Grange airfield, Gosport, on the south coast near Portsmouth, where he was appointed Commanding Officer of No 1 (Reserve) Squadron – a training unit – and took up his appointment there in December 1916.
In the meantime, those aviators who – like Learmount – were a product of the system well ahead of this training upgrade, had to survive with what little skill they had! By the time Learmount was posted, as a 2nd Lieutenant, to No 7 Squadron at Saint-Omer, France, about 25km south-east of Calais, he’d accumulated exactly 24h airborne time. The entry in the “remarks” column of his log book for his 9 June 1915 final training sortie reveals how much the RFC was prepared to forgive to get pilots rapidly to the front line. It says: “Pancaked over sheds, smashed undercarriage and one wing landing.”
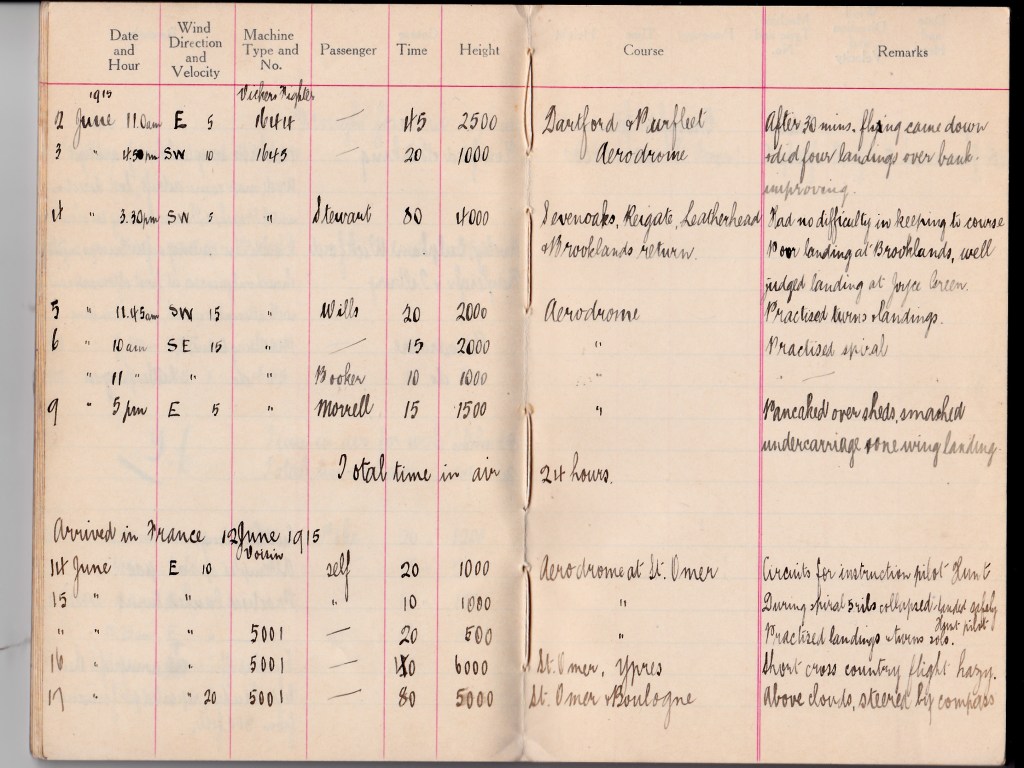
Anyway, the crash-landing at the end of Learmount’s final training sortie was clearly good enough for the RFC, because the next inscription in his log book is: “Arrived in France 12 June 1915.”

Continued tomorrow, Episode 2: Learmount arrives at the RFC aerodrome at Saint-Omer, where he learns to fly a new type and to cope with operations in hostile airspace.