Birdstrikes on airliners are not rare, but they don’t usually cause crashes, let alone fatal ones.
The most famous birdstrike accident before the Jeju Air crash at Muan, Korea a little more than a month ago was the “Miracle on the Hudson”, in which a US Airways Airbus A320 climbing away from take-off at New York LaGuardia airport in January 2009 hit a flock of large geese that disabled both engines. What followed captured the public’s imagination to the extent that Hollywood made a movie about it.
When the geese collided with his aircraft, Captain “Sully” Sullenberger made the decision not to attempt a turn-back to land on the runway, but to glide down for a ditching in the Hudson River. All 155 passengers and crew survived the ditching in the river’s freezing water.
Moving forward 15 years, the Korean aviation and railway and accident investigation board (ARAIB) interim report on the 29 December 2024 Jeju Air crash at Muan International Airport has now confirmed that the chain of events leading to the accident also started with a birdstrike on both engines. The Boeing 737-800, on final approach to runway 01 at Muan, ran into a flock of small ducks which caused the engines and the aircraft extensive damage. Details of the extent and nature of the damage have not been established, but it is clear that some of the aircraft’s electrical systems stopped working.
Much more would normally be known at this stage, but the flight data recorder (FDR) and cockpit voice recorder (CVR) stopped operating at the time of the birdstrike (08:58:50 local time), depriving the investigators of extensive data about the last four minutes of the flight that would otherwise have been captured. Simultaneously the aircraft’s ADS-B transmissions that enable the its three-dimensional trajectory to be tracked in real time also stopped, so it will be more difficult to establish the precise course the crew flew in order to line up for the emergency landing they chose to make.
It was at 08:54:43 that Jeju Flight 7C2216, inbound from Bangkok, Thailand, had first contacted Muan Control Tower and received clearance to land on runway 01. If they had not already done so, at that point they would have selected the undercarriage down and set the flaps for landing.
The first hint of the problems the flight was about to face came four minutes later when the Tower warned the Jeju pilots of bird activity ahead (08:57:50). At that point they were about 3nm from their anticipated landing. The electrical failure that stopped the two recorders occurred a minute later at 08:58:50, at which time the aircraft was still 1.1nm away from the threshold of runway 01, according to the ARAIB report.
The crew saw the flock of ducks ahead and below them just before the birdstrike, it seems, so they decided to abandon the approach and carry out a go-around, increasing engine power and starting to climb away. Six seconds later, at 08:58:56 local time, they declared a Mayday emergency, citing a birdstrike, and announcing their go-around, which had now become far more difficult to carry out because of reduced power from the damaged engines.
The report emphasizes that recordings during the last 4min 7sec of the flight are missing. That is the time that elapsed between the electrical failure that stopped the recorders and the moment of the 737’s violent collision with the earth and concrete mound beyond the end of the landing runway in which the ILS localizer antenna array was embedded (09:02:57).
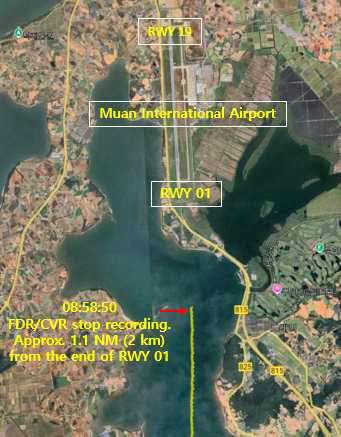
Image from ARAIB interim report
As they initiated their go-around, the pilots felt – and heard – the birdstrike and witnessed a loss of engine thrust just after they had advanced the throttles to climb away. As a part of the go-around drill the crew retracted the undercarriage and selected the flap fully up. There is no recording to confirm this, but they must have done so, as events in the next few minutes make clear.
The attempt to save the flight
The crew knew they had to get the aircraft on the ground fast in case the damaged engines failed completely, but by this time they were losing sight of the runway 01 threshold below the nose as they initiated their go-around, so landing ahead on 01 was no longer an option. Circling back to set up a new approach to the same runway was risky because they might not have sufficient power to maintain height for that long. The ARAIB report says that the last pressure altitude recorded was effectively 500ft (498ft to be precise), and indicated airspeed was 161kt.
At such a point the pilots would want to gain any height and speed they could with the remaining engine power so as to increase their gliding range in the event of total engine failure, and to stay withing gliding range of the runway. So their decision was to fly ahead, then turn through 180deg to land on the same runway but in the opposite direction – that is designated runway 19. Because, during the go-around, they were positioned to the left of runway 01 and parallel to it, they were committing to a right turn to reverse their heading and line up for the approach to 19.
The workload and stress on the pilots at that moment were massive. They did not know how much engine power they would have, or how long they would still have it, so the temptation to turn early to line up on the runway was high. Video of the aircraft’s arrival on runway 19 at Muan shows the aircraft touching down gently with its wings perfectly level, but nearly 2/3rds of the way along the tarmac, travelling very fast with no flaps set, the undercarriage still retracted, and no spoilers deployed.
With the data available at present there is no way of knowing whether the crew failed to get the flap and gear down because of hydraulic problems, or whether the high workload and lack of time made them forget to deploy them. Apart from the failure of electric power to the flight recorders, the investigators don’t know what other problems the pilots faced.
It’s even difficult to work out why an external collision with relatively small birds (Baikal Teals, average weight given as 400g) would cause an electrical supply to fail, unless the undercarriage was still down at the point of birdstrike, leaving electrical wiring and hydraulic tubing in the gear bay vulnerable to impact damage.
Almost all the 181 people on board the Jeju 737 were killed, the only survivors being two cabin crew strapped into their seats in the tail of the aircraft. Everyone on board would still have been alive until the high speed impact with the solid foundations for the ILS localiser antenna array about 200m into the runway overrun, which caused the aircraft to break up and catch fire.
If they had hydraulics, surely there would have been a strong human instinct from the pilots the use the rudder to yaw the plane, instead of plowing straight into the embankment. Yes this would likely have resulted in a roll and the plane breaking up, however the energy would have been dissipated over a longer timeframe. To me the fact they didn’t do this suggests that they had no control.
LikeLike
There is also the possibility that the pilots thought the localiser antenna array would collapse on impact, as it should normally be designed to do.
LikeLike